Portal:Renewable energy
Introduction Renewable energy (or green energy) is energy from renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind power and hydropower. Bioenergy and geothermal power are also significant in some countries. Some also consider nuclear power a renewable power source, although this is controversial. Renewable energy installations can be large or small and are suited for both urban and rural areas. Renewable energy is often deployed together with further electrification. This has several benefits: electricity can move heat and vehicles efficiently, and is clean at the point of consumption. Variable renewable energy sources are those that have a fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power. In contrast, controllable renewable energy sources include dammed hydroelectricity, bioenergy, or geothermal power. Renewable energy systems have rapidly become more efficient and cheaper over the past 30 years. A large majority of worldwide newly installed electricity capacity is now renewable. In most countries, photovoltaic solar or onshore wind are the cheapest new-build electricity. From 2011 to 2021, renewable energy grew from 20% to 28% of global electricity supply. Power from sun and wind accounted for most oft his increase, growing from a combined 2% to 10%. Use of fossil energy shrank from 68% to 62%. In 2022, renewables accounted for 30% of global electricity generation, and are projected to reach over 42% by 2028. Many countries already have renewables contributing more than 20% of their total energy supply, with some generating over half or even all their electricity from renewable sources. The main motivation to replace fossil fuels with renewable energy sources is to slow and eventually stop climate change, which is widely agreed to be caused mostly by greenhouse gas emissions. In general, renewable energy sources cause much lower emissions than fossil fuels. In 2022 the International Energy Agency (IEA) requested all countries to reduce their policy, regulatory, permitting and financing obstacles for renewables. This would increase the chances of the world reaching net zero carbon emissions by 2050. According to the IEA, to achieve net zero emissions by 2050, 90% of global electricity generation will need to be produced from renewable sources. The deployment of renewable energy still faces obstacles, especially fossil fuel subsidies, lobbying by incumbent power providers, and local opposition to the use of land for renewables installations. Although most renewable energy sources are sustainable, some are not. For example, some biomass sources are unsustainable at current rates of exploitation. (Full article...) Selected article -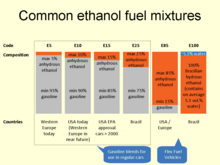 Ethanol fuel is fuel containing ethyl alcohol, the same type of alcohol as found in alcoholic beverages. It is most often used as a motor fuel, mainly as a biofuel additive for gasoline. Several common ethanol fuel mixtures are in use around the world. The use of pure hydrous or anhydrous ethanol in internal combustion engines (ICEs) is only possible if the engines are designed or modified for that purpose. Anhydrous ethanol can be blended with gasoline (petrol) for use in gasoline engines, but with high ethanol content only after engine modifications to meter increased fuel volume since pure ethanol contains only 2/3 the energy of an equivalent volume of pure gasoline. High percentage ethanol mixtures are used in some racing engine applications as the very high octane rating of ethanol is compatible with very high compression ratios. The first production car running entirely on ethanol was the Fiat 147, introduced in 1978 in Brazil by Fiat. Ethanol is commonly made from biomass such as corn or sugarcane. World ethanol production for transport fuel tripled between 2000 and 2007 from 17×109 liters (4.5×109 U.S. gal; 3.7×109 imp gal) to more than 52×109 liters (14×109 U.S. gal; 11×109 imp gal). From 2007 to 2008, the share of ethanol in global gasoline type fuel use increased from 3.7% to 5.4%. In 2011 worldwide ethanol fuel production reached 8.46×109 liters (2.23×109 U.S. gal; 1.86×109 imp gal) with the United States of America and Brazil being the top producers, accounting for 62.2% and 25% of global production, respectively. US ethanol production reached 57.54×109 liters (15.20×109 U.S. gal; 12.66×109 imp gal) in May 2017. (Full article...)Quotations -
– Lester R. Brown. PLAN B 3.0: Mobilizing to Save Civilization 2008, p. 215. Main topicsRenewable energy sourcesGeneralRenewable energy commercialization · Smart grid · Timeline of sustainable energy research 2020–present Renewable energy by countryList of countries by electricity production from renewable sources
WikiProjectsWikiProjects connected with renewable energy: Selected image - Rapeseed field at Grendon, Northamptonshire. Rapeseed oil is used in the manufacture of biodiesel for powering motor vehicles. Selected biography -Elon Reeve Musk (/ˈiːlɒn/ EE-lon; born June 28, 1971) is a businessman and investor. He is the founder, chairman, CEO, and CTO of SpaceX; angel investor, CEO, product architect, and former chairman of Tesla, Inc.; owner, executive chairman, and CTO of X Corp.; founder of The Boring Company and xAI; co-founder of Neuralink and OpenAI; and president of the Musk Foundation. He is one of the wealthiest people in the world; , Forbes estimates his net worth to be US$196 billion. A member of the wealthy South African Musk family, Musk was born in Pretoria and briefly attended the University of Pretoria before immigrating to Canada at age 18, acquiring citizenship through his Canadian-born mother. Two years later, he matriculated at Queen's University at Kingston in Canada. Musk later transferred to the University of Pennsylvania and received bachelor's degrees in economics and physics. He moved to California in 1995 to attend Stanford University, but dropped out after two days and, with his brother Kimbal, co-founded online city guide software company Zip2. The startup was acquired by Compaq for $307 million in 1999. That same year, Musk co-founded X.com, a direct bank. X.com merged with Confinity in 2000 to form PayPal. In October 2002, eBay acquired PayPal for $1.5 billion. Using $100 million of the money he made from the sale of PayPal, Musk founded SpaceX, a spaceflight services company, in 2002. (Full article...)Did you know? -... that the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) published Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation (SRREN) in May 2011 ? The IPCC examined renewable energy and energy efficiency in its fourth assessment report, published in 2007, but members have now decided that renewable energy commercialization merits in-depth coverage because of its importance in reducing carbon emissions. General images -The following are images from various renewable energy-related articles on Wikipedia.
Related portalsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |
































![Image 30Concentrated solar panels are getting a power boost. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) will be testing a new concentrated solar power system – one that can help natural gas power plants reduce their fuel usage by up to 20 percent.[needs update] (from Solar energy)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/82/Photo_of_the_Week-_Boosting_Solar_Technology_%288722948189%29.jpg/120px-Photo_of_the_Week-_Boosting_Solar_Technology_%288722948189%29.jpg)















































